By: Dina Ali, Megan E. Barra, Joseph Blunck, Gretchen M. Brophy, Caitlin S. Brown, Meghan Caylor, Sarah L. Clark, David Hensler, Mathew Jones, Amanda Lamer-Rosen, Melissa Levesque, Leana N. Mahmoud, Sherif H. Mahmoud, Casey May, Keith Nguyen, Nicholas Panos, Christina Roels, Justin Shewmaker, Keaton Smetana, Jessica Traeger, Aric Shadler & Aaron M. Cook
Published: 04 November 2020
Background/Objective
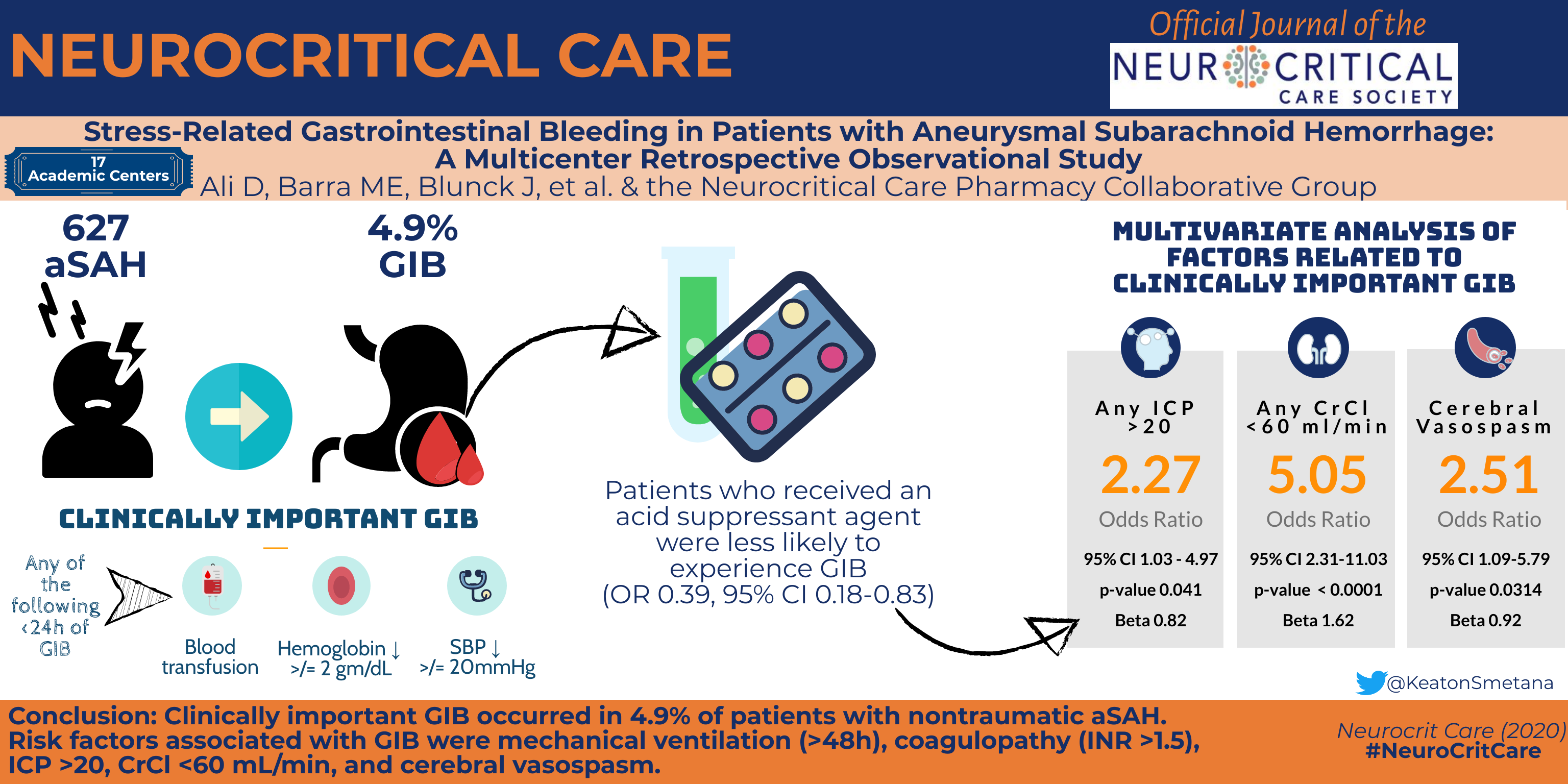
Stress-related mucosal bleeding (SRMB) occurs in approximately 2–4% of critically ill patients. Patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH) have a (diffuse) space-occupying lesion, are critically ill, often require mechanical ventilation, and frequently receive anticoagulation or antiplatelet therapy after aneurysm embolization, all of which may be risk factors for SRMB. However, no studies have evaluated SRMB in patients with aSAH. Aims of the study were to determine the incidence of SRMB in aSAH patients, evaluate the effect of acid suppression on SRMB, and identify specific risk factors for SRMB.
Methods
This was a multicenter, retrospective, observational study conducted across 17 centers. Each center reviewed up to 50 of the most recent cases of aSAH. Patients with length of stay (LOS) < 48 h or active GI bleeding on admission were excluded. Variables related to demographics, aSAH severity, gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, provision of SRMB prophylaxis, adverse events, intensive care unit (ICU), and hospital LOS were collected for the first 21 days of admission or until hospital discharge, whichever came first. Descriptive statistics were used to analyze the data. A multivariate logistic regression modeling was utilized to examine the relationship between specific risk factors and the incidence of clinically important GI bleeding in patients with aSAH.
Read the article.